



Next: Optimization of General Coordinates
Up: Program Relax
Previous: Program Relax
Contents
Index
relax drives and controls a non-linear optimization procedure to
locate the minimum (or a stationary point) of a function f (x). In
TURBOMOLE f is always the electronic energy, and the coordinates
x will be referred to as general coordinates. They include
- cartesian atomic coordinates
- internal atomic coordinates
- exponents, contraction coefficients and scaling factors of basis
functions
- a global scaling factor (a common scaling factor for all basis
set exponents)
The optimization employs an iterative procedure based on gradients
∇f of the current and, if available, previous iterations.
Various procedures can be applied: steepest descent, Pulay's
DIIS, quasi-Newton, conjugate
gradients, as well as combinations of them.
relax carries out:
- update of general coordinates
- update of approximate hessians if needed
- conversion of coordinates (internal
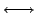 cartesian)
cartesian)
The mode of operation is chosen by the keywords $optimize and
$interconversion and the corresponding options, which will
be described in the following sections.
TURBOMOLE